What is a tooth abscess?
What is an abscessed tooth?
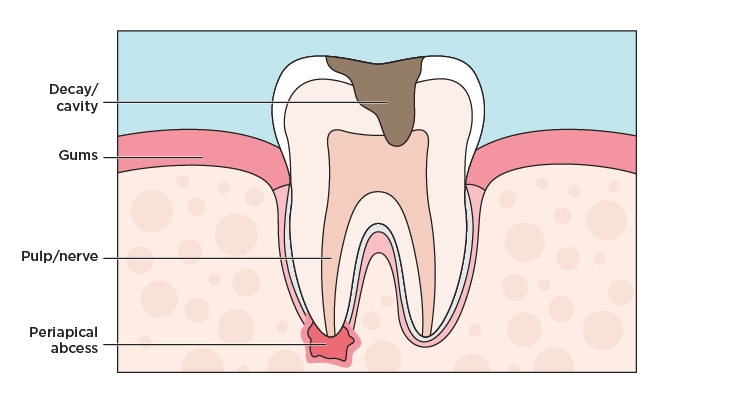
Openings in enamel allow bacteria to grow and infect the center of a tooth, which can spread from the root to the supporting bones. This type of infection results in a tooth abscess, also known as a dental abscess, which is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection and often resulting in a painful toothache. There are two types of tooth abscesses: periapical and periodontal.
Abscesses can occur at different areas around the tooth for different reasons – a periapical abscess occurs at the tip of the root, while a periodontal abscess occurs in the gums at the side of a tooth root. A periapical tooth abscess typically occurs because of an untreated dental cavity, an injury, or prior dental work.
Abscessed tooth signs and symptoms
- Severe, constant, throbbing toothache that can spread to your jawbone, neck, or ear
- Pain or discomfort with hot and cold temperatures
- Pain or discomfort with the pressure of chewing or biting
- Fever
- Swelling in your face, cheek, or neck that may lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck
- Foul odor in your mouth
- A sudden rush of foul-tasting, salty fluid in your mouth and pain relief, if the abscess ruptures
You should see your dentist as soon as possible if you begin to see any signs or symptoms of a tooth abscess. If you have a fever, swelling in your face, trouble breathing or swallowing, and you can't reach your dentist, then go to an emergency room as these symptoms often indicate the infection has spread deeper into your jaw, throat, neck, or other areas of your body.
How do you treat a tooth abscess?
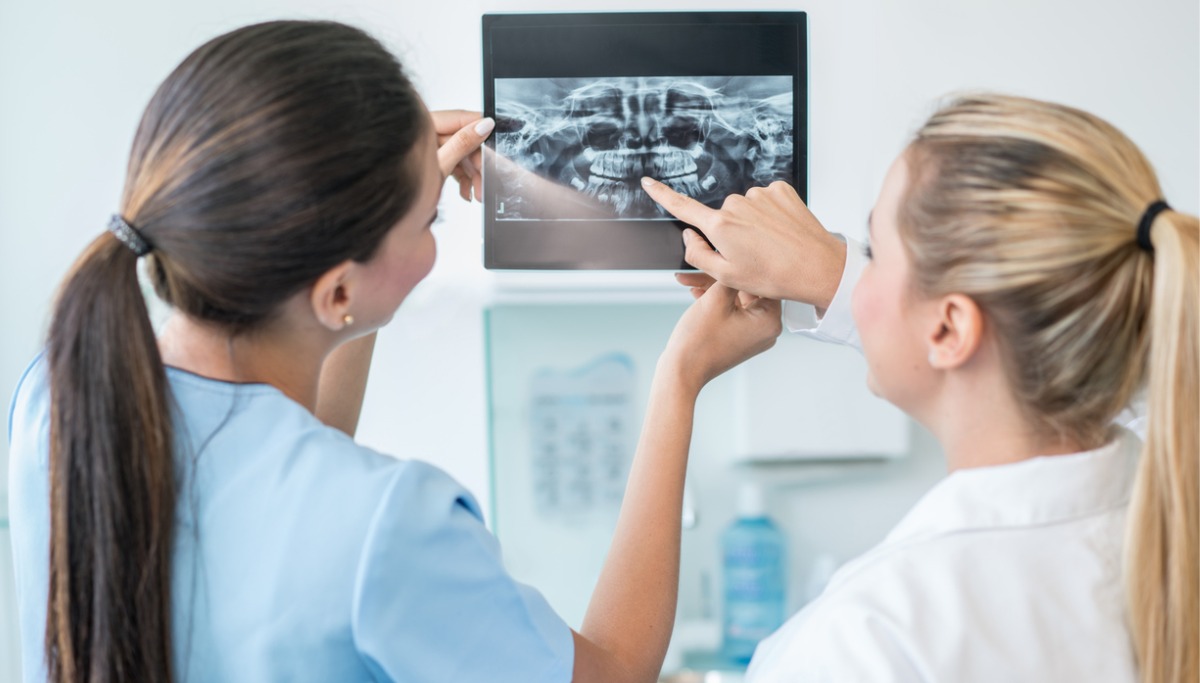
To properly diagnose an abscess, your dentist will look closely at your teeth, mouth, and gums. Dental radiographs and other tests can help your dentist determine which tooth or teeth are causing the problem. To get rid of the infection, your dentist might provide antibiotics before draining the abscess. The tooth might be salvageable with root canal treatment, but in some cases, the tooth may need to be pulled.
What causes a tooth abscess?
There are multiple causes of tooth abscesses, including:
- Poor dental habits and care – Not taking proper care of your teeth and gums can increase your risk of dental problems.
- A diet high in sugar – Frequently eating and drinking foods rich in sugar, such as sweets and sodas, can contribute to dental cavities and turn into a tooth abscess.
- Dry mouth – A dry mouth can increase your risk of tooth decay.
What happens if you leave a tooth abscess untreated?
Leaving a tooth abscess untreated can lead to serious, even life-threatening, complications. If the abscess is not drained in time, then it can rupture. A ruptured abscess will relieve the pressure, but the infection will remain active and continue to spread, causing more pain and destroying tissue. Additionally, these infections can spread to other parts of the body and cause bone infections, sepsis, blood infections, cellulitis, and even parapharyngeal (deep neck) abscesses.
How to prevent a tooth abscess
To prevent a tooth abscess and decay, it is essential to take proper care of your teeth by:
- Drinking water that contains fluoride.
- Brushing your teeth two times a day, every day, for two minutes with fluoride toothpaste.
- Using dental floss to clean between your teeth daily.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, and whenever you are sick.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and limiting sugary items.
- Visiting your dentist every six months for checkups and cleanings.
Sources:
- Tooth Abscess. (2022, June 29) from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
- Tooth Abscess. (2022, January 24) from https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess
- What Happens If Your Tooth Root Infection Is Left Untreated? (2021, January 12) from https://fineartsdentistry.com/what-happens-if-your-tooth-root-infection-is-left-untreated/